
by Randy Horton and Ken Jones
Smartphones are Everywhere
Mobile devices have become a ubiquitous part of modern life. In 2022, there were over 307 million smartphone users in the U.S.
The ubiquitous nature of the smartphone (which includes a powerful local computer, touchscreen interface, rich network connectivity upstream to the Internet and downstream to Internet of Things devices, and a powerful array of embedded physical sensors, out-of-the-box) makes it a perfect tool for medical monitoring, diagnostics, and therapeutics (i.e., treatment).
This article includes an analysis of the trends for smartphones, and specifically Bluetooth versions, that have a major impact on the software that operates smartphones in conjunction with connected medical devices such as insulin pumps, glucose monitors, active implanted surgical devices, hearing aids and devices that rapidly diagnose infectious disease. The trends are pulled from ScientiaMobile’s Mobile Overview Report (MOVR) from 2023 Q1, and our predictions are based on a longitudinal analysis of MOVR data.
Increasing Fragmentation of Smartphone Models
While most people carry a smartphone, the variety of smartphones is growing, posing a challenge in developing software that can effectively utilize the capabilities of these devices.
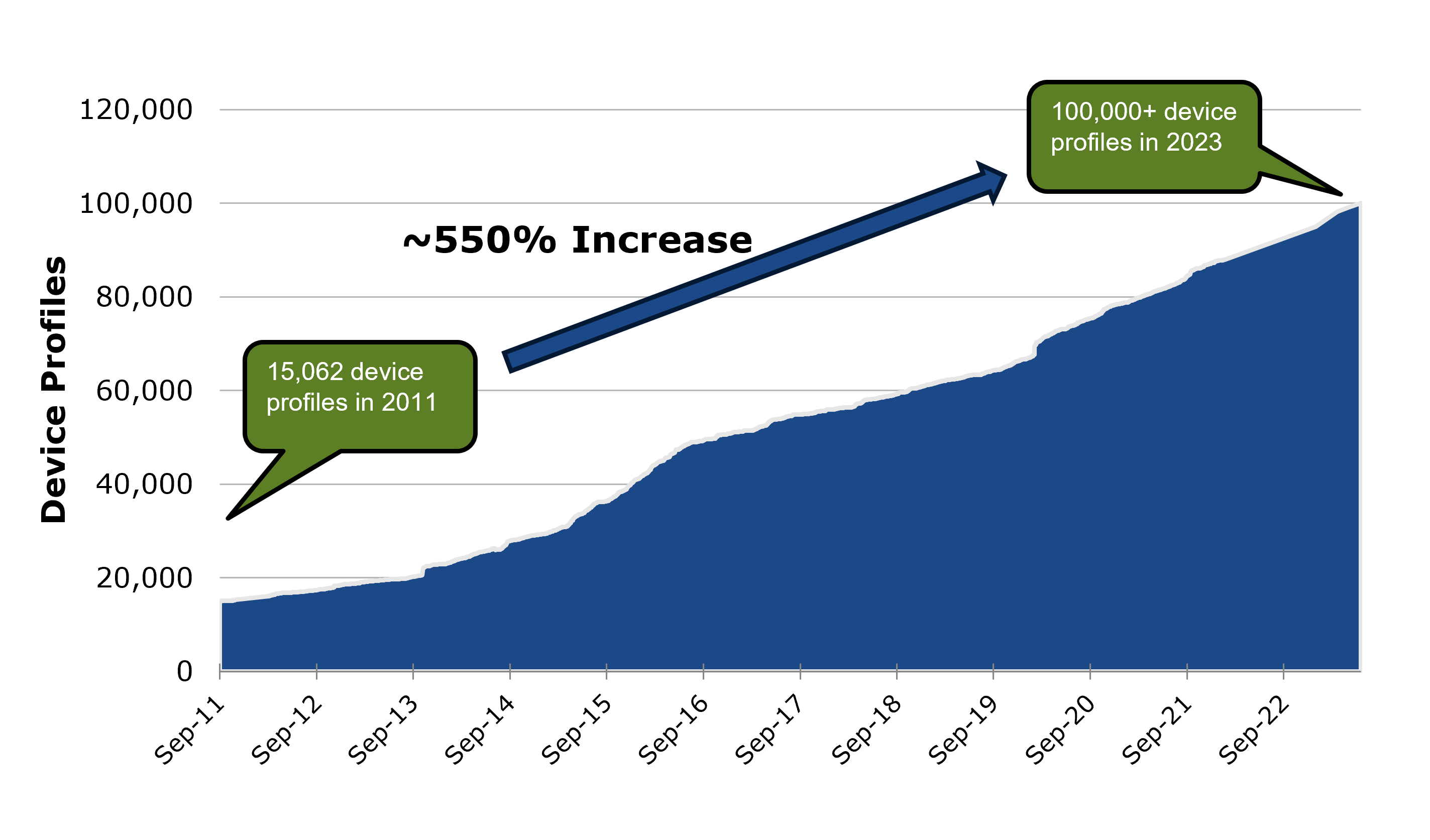
Since 2011, the number of mobile device model profiles (a unique combination of brand, model, and operating system version) tracked by ScientiaMobile’s WURFL device detection software has increased by over 550%, reaching more than 100,000 devices globally in 2023. (See figure below.) To further illustrate the massive increase in variation of smartphone versions in use, this analysis does not even account for the numerous combinations of unique web browser applications and their versions used on any given mobile device profile.
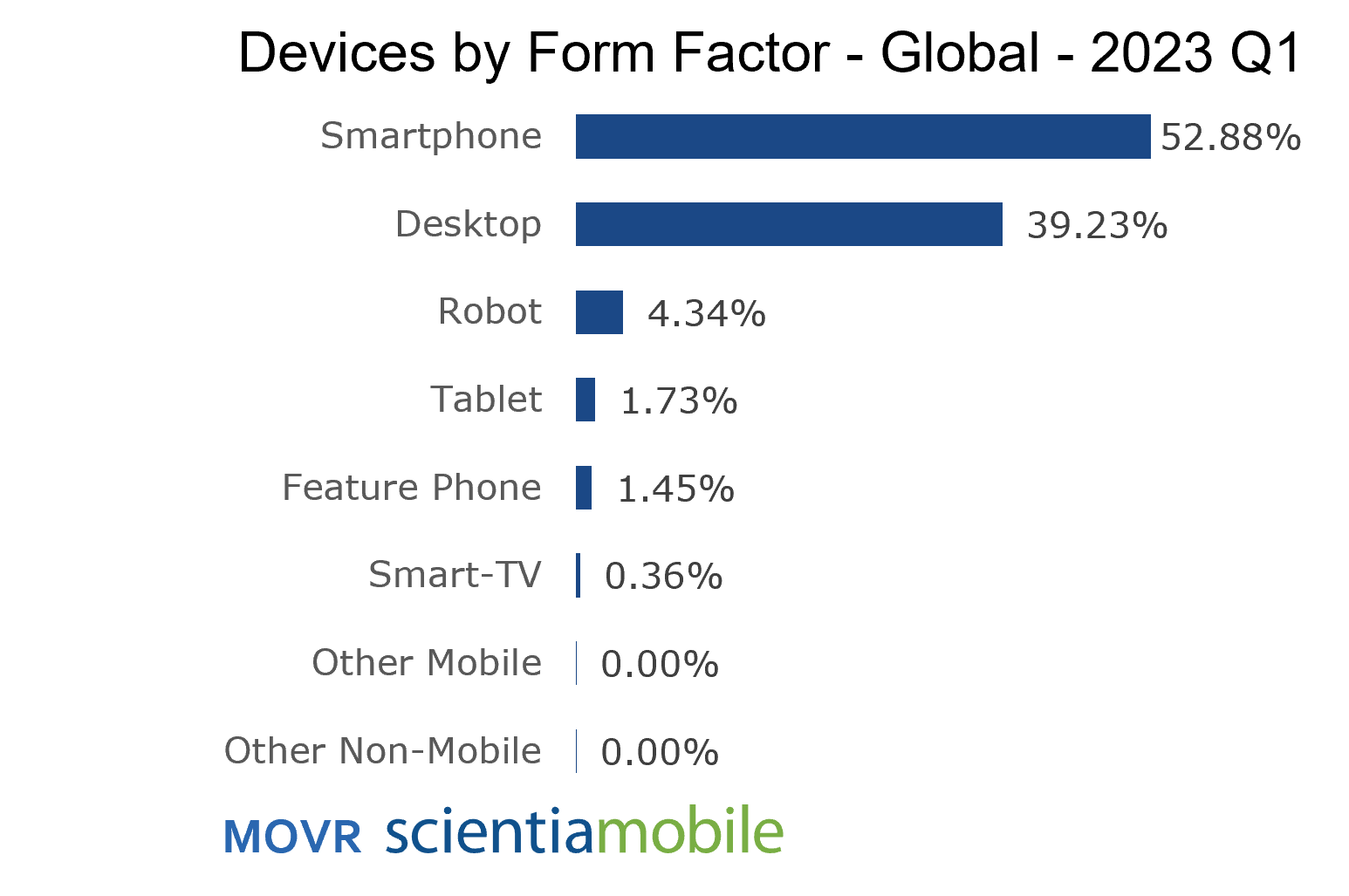
This fragmentation is a significant issue for developers when we consider that 52.8% of all device usage seen on the web came from smartphones in 2023 Q1. (See figure below.)
Clearly, this level of fragmentation poses problems for developers looking to cover as wide an audience as possible. There are thousands of device models in use today. While many are less than two years old, there are also many that were released years ago and have older technology. Software developers must make decisions about how much of this old technology they will support in their software. The greater the amount of old technology support, the higher the development and maintenance costs.
Measuring the usage of smartphones and evaluating the commonality of critical features, like Bluetooth versions, provides critical insight for software developers. The MOVR issued by ScientiaMobile on a quarterly basis provides analysis of mobile device usage trends.
Android Smartphones Drive Model Fragmentation
In general, there are two flavors of smartphones determined by their operating system (OS): Android or iOS. Globally, Android holds the majority share, accounting for 63% of all usage.
However, in the U.S. and Canada, iOS is more popular with a 55% market share compared to Android’s 45% in 2023 Q1.
In general, Android smartphones are more affordable compared to Apple’s iPhones, which exclusively run on iOS. While Apple has succeeded in holding the premium price market segment, that dominance is slowly eroding.
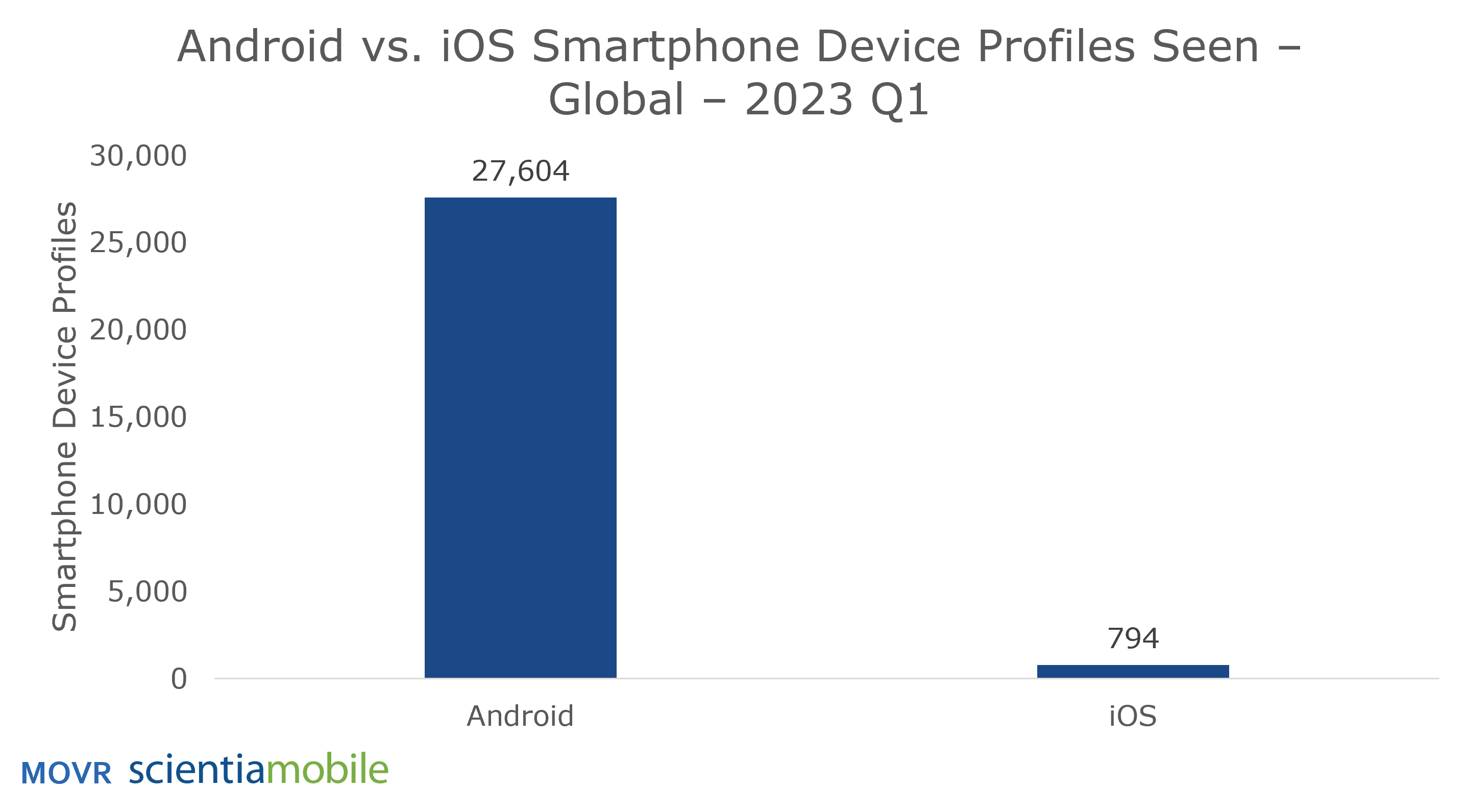
On the iOS side, Apple releases a limited number of iPhone models, typically around 3 to 5 models per year. As a result, there is a relatively low number of device profiles (combinations of device models, operating system versions) for iOS. In contrast, there are many manufacturers releasing different smartphone models running on the Android platform. In 2023 Q1, MOVR observed 27,604 different smartphone device profiles running Android globally, while there were only 794 iOS device profiles. It is evident that the challenge of managing smartphone device fragmentation for developers primarily stems from Android-based devices.
Bluetooth is a Critical Capability for Medical Software
Bluetooth is a wireless protocol that enables connectivity between devices. Almost all smartphones available today include Bluetooth capabilities. According to the industry group Bluetooth SIG, 100% of new smartphones shipping today now include Bluetooth support. However, Bluetooth comes in different versions. The Bluetooth version is critical for specific types of connected medical devices for a number of reasons:
The Bluetooth Low-Energy (or BLE) technology was introduced with Bluetooth 4.x. BLE allows external devices running on battery power to last longer before requiring recharging or replacement. This is particularly significant for scenarios involving surgically implanted devices that regularly communicate with a patient’s smartphone. Right now, these devices often depend on a battery in the surgically implanted device for power, and when the battery runs out, it requires another procedure to replace the battery. Therefore, every extra day/month of battery life has a significant impact on the patient’s health and the overall cost of care. BLE support has become universal with Bluetooth 5.x and works in tandem with the features of Bluetooth 5 discussed in the following bullets.
Bluetooth 5.x doubles the transmission rates compared to Bluetooth 4.x, increasing from 1 Mbps to 2 Mbps. This difference is especially significant for medical devices that need to continually transmit high volumes of data, such as the waveform data generated by cardiac and respiratory monitors (see diagram below).
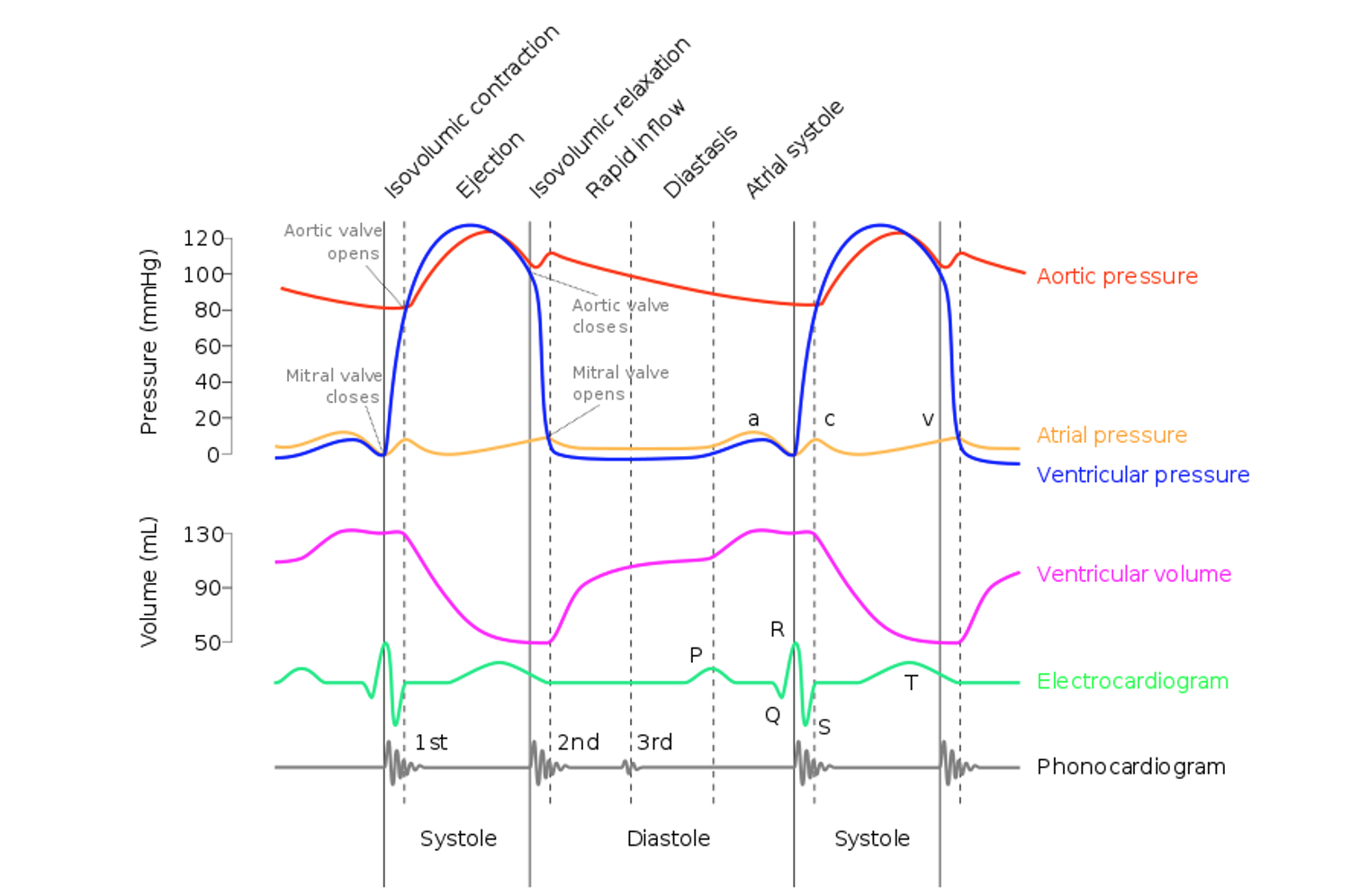
Above: An example of a Wiggers diagram, showing the cardiac cycle events occurring in the left ventricle. Source: Wikimedia
Bluetooth 5.x supports communication between a smartphone and an external device within a range of 800 feet under optimal physical circumstances, whereas Bluetooth 4.x had a limited range of 200 feet. While this may be a use case of lesser importance, the benefits can be substantial. For example, it makes it easier for a parent’s smartphone to communicate with a child’s continuous glucose monitor or insulin pump across a public park.
Bluetooth 5.x enables valuable new functionality in devices such as hearing aids, allowing for bi-directional communication between hearing aids and smartphones. In contrast, Bluetooth 4.x only allowed the connected device to stream to the hearing aids without the capability for two-way communication. As a result, hands-free calling wasn’t possible with Bluetooth 4.x since the hearing aid microphone couldn’t capture the user’s voice and transmit it to the phone.
iPhone Bluetooth Support Trends
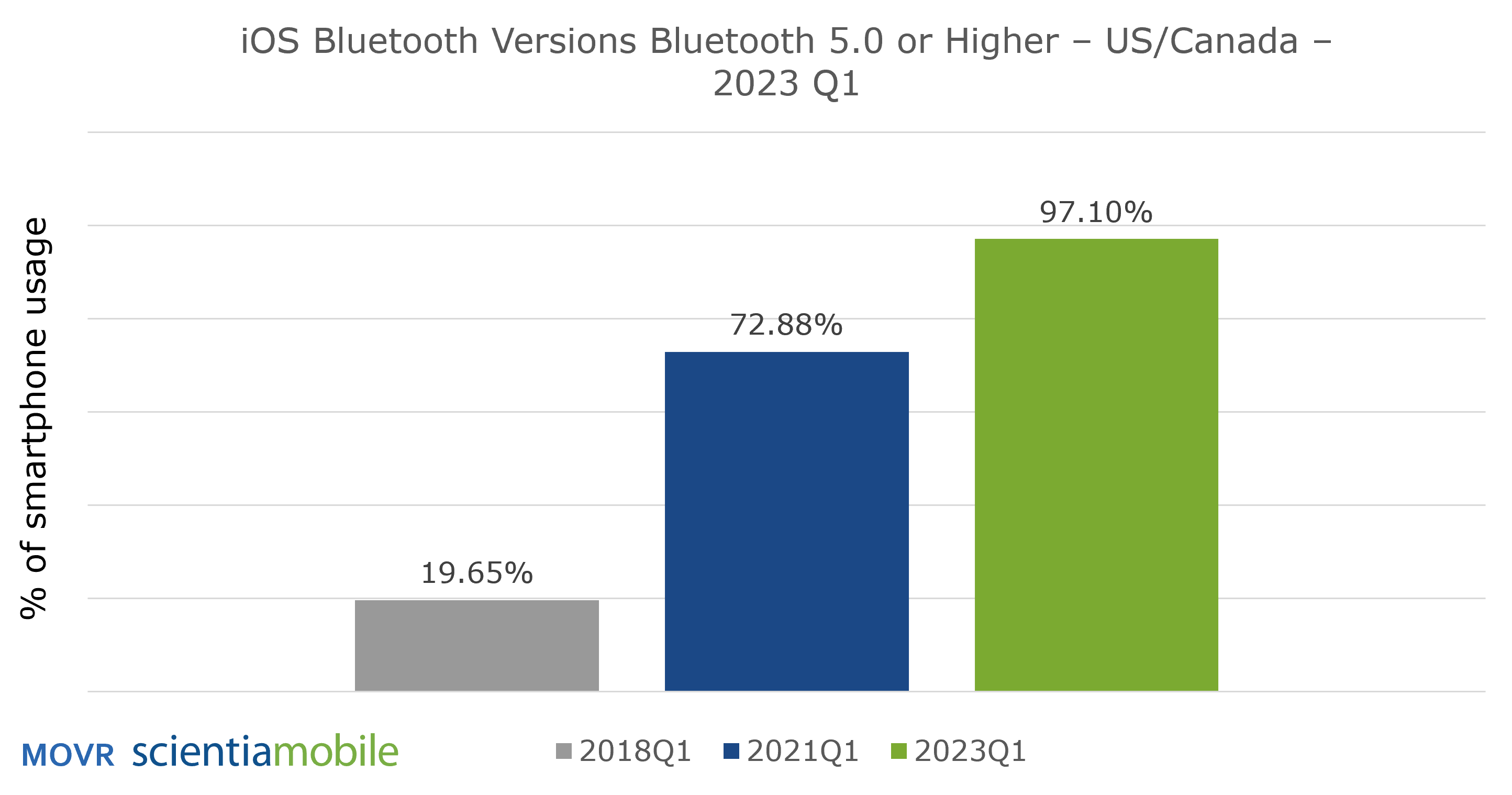
Looking at iPhones running iOS in 2023 Q1 in the U.S. and Canada, it was found that 97.10% of them are utilizing Bluetooth version 5.x or higher (see below).
Android Bluetooth Support Trends
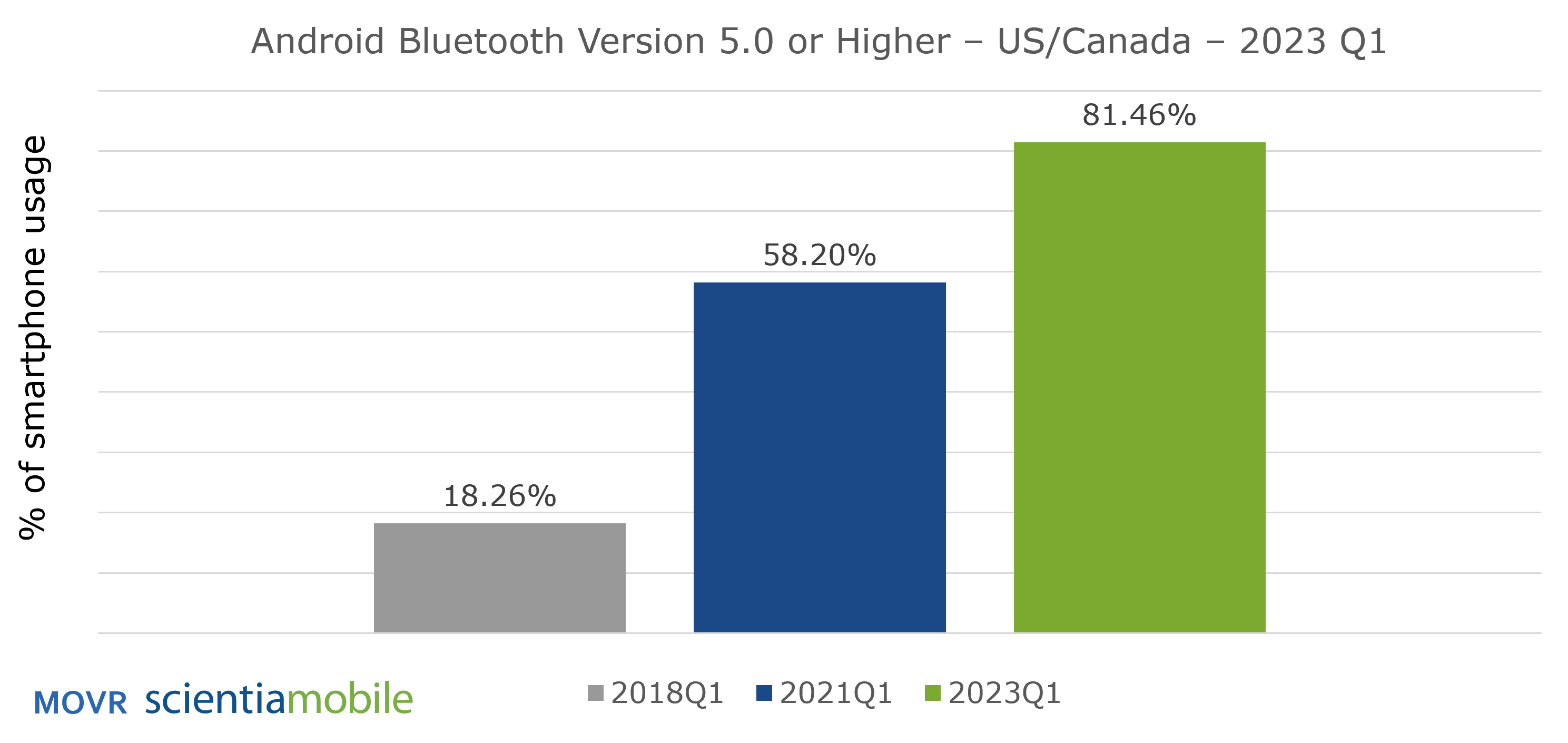
In contrast, Android smartphones are more fragmented and lag behind in terms of Bluetooth capabilities. The percentage of Android smartphones with Bluetooth 5.x or higher grew from 58.20% in 2021 Q1 to 81.46% in 2023 Q1.
Software Development Choices
At the time of the original publication of our article, the lower level of penetration of Bluetooth 5 in both Android and iOS smartphones posed challenges for development. Connected medical device manufacturers were unable to leverage all of the new features offered by Bluetooth 5.x due to the need for backward compatibility with older smartphones still operating on 4.x versions.
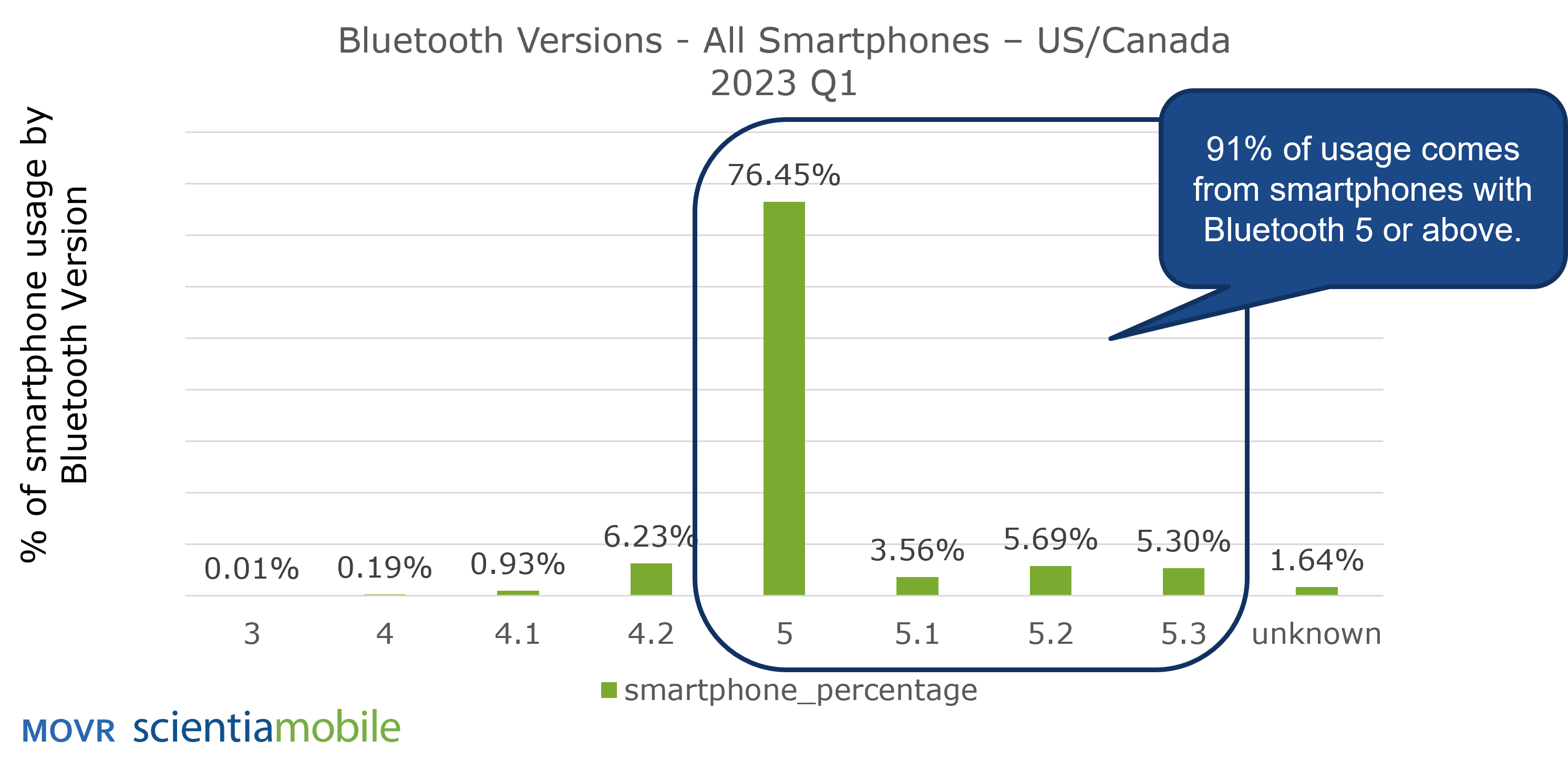
However, as the adoption of Bluetooth 5.x has exceeded 91% of all devices in the U.S. and Canada, with that number projected to reach 95% by the end of 2023, medical device manufacturers no longer need to be concerned about sacrificing a significant portion of the market in order to avail themselves of valuable new functionality. They can safely focus on developing software that uses Bluetooth 5.x without the burden of backward compatibility.
Age and Replacement of Smartphones
GIven that Android represents the majority of the remaining smartphones still running on a version below Bluetooth 5.x, an important question arises: How long will it take for these devices to be replaced with newer phones so that Bluetooth 5.x adoption rates for Android phones in the U.S. match the >90% adoption rate seen with iPhones?
Out of these smartphones with Bluetooth versions below 5.x, 71.33% fall into the category of being 37+ months old. This subset of smartphones below Bluetooth 5.x is twice the size of the average across all smartphones.
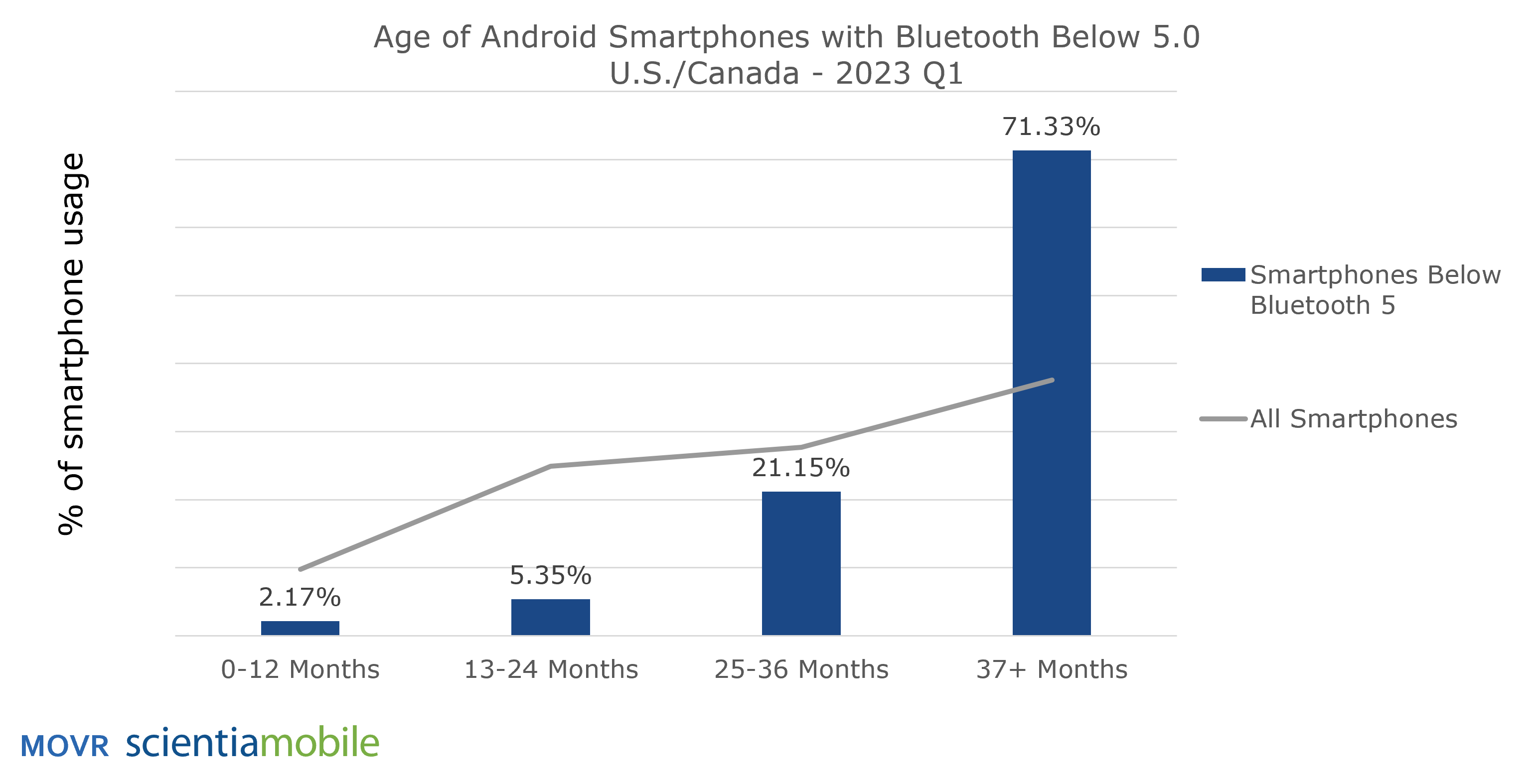
It is highly probable that a large portion of these older smartphones will be replaced within the next year by new phones with Bluetooth 5.x or higher.
More than 54% of Android smartphones in the U.S. and Canada are replaced every 24 months, resulting in an upgrade of the Bluetooth capabilities within the general population through newer smartphones. When looking at the ages of phones based on their release date, there are occasional spikes that align with major conferences (e.g., Mobile World Congress) or peak sales seasons (e.g., Christmas) in the mobile phone industry.
Having said that, a long tail of older phones will persist. The key questions are, how long will this tail be and how large will it grow?
By extrapolating based on the replacement rate of older smartphones over time, we can estimate how quickly Bluetooth 4.x Android devices will phase out of service. In our original report in 2021, we projected that by 2023, Bluetooth 4.x or older devices would account for about 5% of the Android smartphone market. Given that we have already reached 91% of all smartphones with Bluetooth 5.x in 2023 Q1, we are confident that this number will reach 95% by the end of 2023. This development should be beneficial for many medical device developers, simplifying the need for multiple versions and expanding the potential market size.
Pricing of Bluetooth Versions on Android
In general, Bluetooth is not a marquis feature for smartphones. Manufacturers don’t differentiate their smartphone models by advertising the sophistication of their internal Bluetooth chips and implementations. To save production costs, low-end smartphone manufacturers will opt for an older version of Bluetooth in their budget-friendly phones in order to make them more affordable (see figure below).

Almost 80.53% of smartphones that currently have Bluetooth versions below 5.x are less than $400 in price. Going forward, it is expected that most new phones even in the low-price range will receive Bluetooth 5 or higher if it is included in the primary SoC chipset.
Conclusion
Bluetooth 5.x marks a major step forward for medical device software developers. The 91% adoption rate of Bluetooth 5.x as the minimum standard on smartphones in the U.S, with a projected growth to 95% by the end of 2023, offers an enormous advantage for medical device software developers and medical device manufacturers. It relieves them of the burden of managing version-specific features and backward compatibility, enabling them to take advantage of the new functionality enabled with Bluetooth 5.x.
Methodology on How ScientiaMobile Defines the Data
Sample Sizes
U.S. + Canada – all device form factors (desktop + smartphone + tablet + smart TV)
2018Q1: 1,416,850,874
2021Q1: 923,152,048
2023Q1: 684,760,903
U.S. + Canada – smartphone only
2018Q1: 449,141,727
2021Q1: 304,636,172
2023Q1: 186,205,710
What is a device profile? A device profile in the WURFL device detection solution is a unique combination of device brand, model, and operating system.
What is a usage observation in the data? How is that different from the devices sold? A usage observation, also known as a “hit”, happens each time a user visits a Web page and a user agent (UA) is generated and tested by WURFL (through a number of mechanisms). All data reported in MOVR reflects hits, not the count of unique physical devices generating those hits.
References
2019 Bluetooth Market Update, Bluetooth SIG, https://www.bluetooth.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/2019-Bluetooth-Market-Update.pdf
“Bluetooth 5: Is it actually better, and do you need it?” Android Central, https://www.androidcentral.com/bluetooth-5-it-actually-better-and-do-you-need-it
“Best Bluetooth Hearing Aids of 2023 for Android and iOS”, Hearing Central, https://www.hearingtracker.com/bluetooth-hearing-aids
About the Authors
Ken Jones, Vice President of Solutions, ScientiaMobile
Ken Jones is Vice President of Solutions at ScientiaMobile with 20 years of demonstrated results in the web, telecommunications, and software industry both as a marketer and consultant. He is skilled in financial modeling, market sizing, mobile advertising, location-based services, IPTV, fixed-mobile convergence, IMS, telecommunications sourcing, SIP and VoIP, and competitive analysis.
Jones holds an M.B.A. from Northwestern University’s Kellogg School of Management and B.A. from Northwestern University.
Randy Horton, Chief Solutions Officer, Orthogonal
Randy Horton is Chief Solutions Officer at Orthogonal, a software consulting firm that improves patient outcomes faster by helping MedTech firms accelerate their development pipelines for Software as a Medical Device (SaMD), digital therapeutics (DTx) and connected medical device systems. Orthogonal makes that acceleration happen by fusing modern software engineering and product management tools and techniques (e.g., Agile, Lean Startup, User-Centered Design and Systems Thinking) with the regulated focus on device safety and effectiveness that is at the heart of MedTech.
Horton serves as Co-Chair for AAMI’s Cloud Computing Working Group, as well as AAMI CR:510(2021) and the in-process Technical Information Report #115, all of which address how to safely move medical device computing functions into the cloud. He is a frequent speaker at conferences and webinars, including events hosted by AdvaMed, AAMI, HLTH, RAPS and the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society (HFES).
About ScientiaMobile
ScientiaMobile provides accurate mobile device intelligence and image optimization solutions that improve the mobile experience and make web pages load faster.
ScientiaMobile was formed in 2011 to commercialize WURFL, the industry’s most advanced device detection solution. With customers such as Google, Amazon, and Akamai, ScientiaMobile’s device detection helps drive more than 83% of the internet’s device analytics. ScientiaMobile continues to lead the mobile device intelligence market and leverage this core competency to expand into new markets. In 2015, ScientiaMobile launched ImageEngine, a smart image CDN, which accelerates websites by 60%. ScientiaMobile is the winner of the Red Herring Top 100 Global and Inc 5000 awards.
About Orthogonal
Orthogonal is a software developer that improves patient outcomes faster by helping MedTech firms accelerate their development pipelines for Software as a Medical Device (SaMD), Digital Therapeutics (DTx) and connected medical device systems. The way we do this is by fusing modern software development and product management techniques developed in other industries (such as Agile, Lean Startup, User-Centered Design and Systems Thinking) with the regulated focus on safety and effectiveness that is at the heart of the medical device sector. Over the last ten years, we’ve helped a wide variety of firms develop and bring their regulated/connected devices to market.








